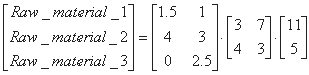|
MasterAllRound: the PC calculator |
Matrices: matrix multiplication: economics exampleSolving econimics problems often involves matrix calculations. Let's assume you have the task of determining the amount of raw material necessary to produce two different products. The final products in turn consist of intermediate products. The problem is interlinked with the amount of raw material, intermediate product and final product. To solve the problem, we need to perform multiple matrix multiplication. Let's assume the following for our two final products:
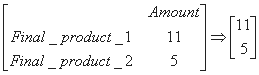
To produce these two final products, the following amounts of intermediate products are necessary:
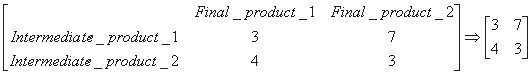
Again, to produce the intermediate product, the following amount of raw material is necessary:
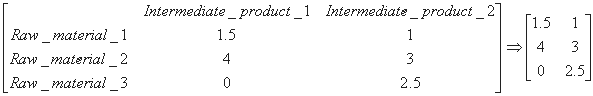
In matrix formulation, we have to solve the following problem:
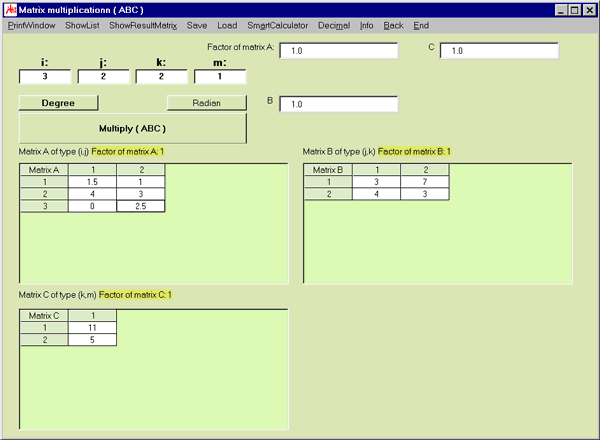
The course of action with MasterAllRound is:
|
| © 2018 MAR Team - all rights reserved |